Blount Disease Vs Rickets
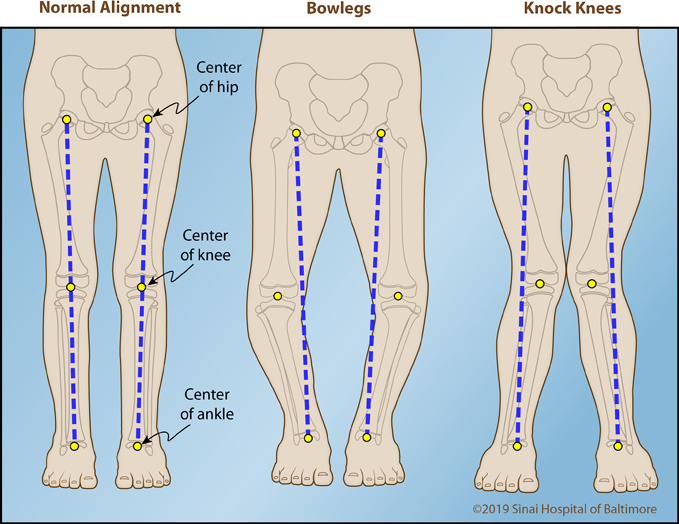
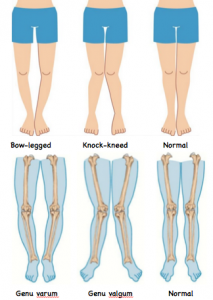
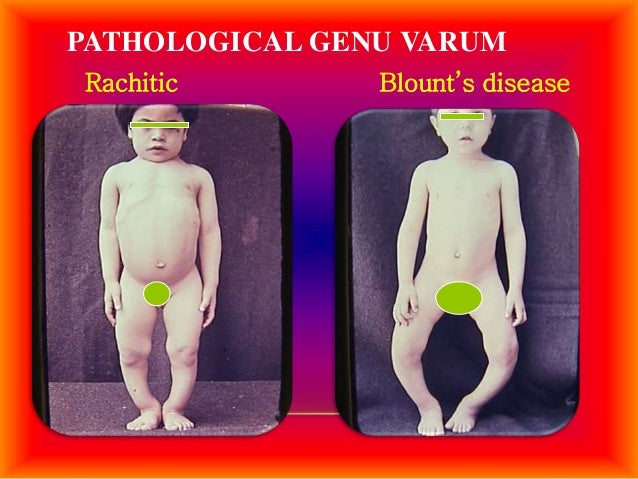
Blount disease vs rickets. The condition is commonly bilateral. While it is not uncommon for young children to have bowed legs typically the bowing improves with age. It can result from a vitamin D deficiency.
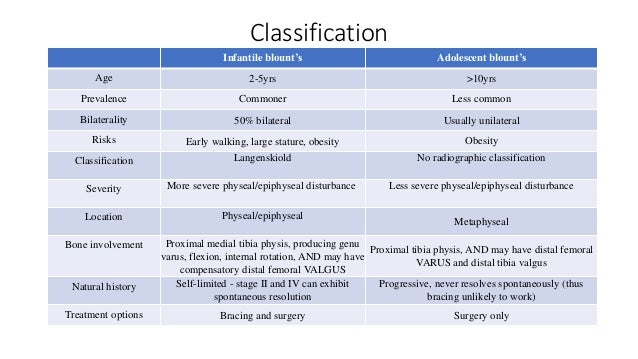
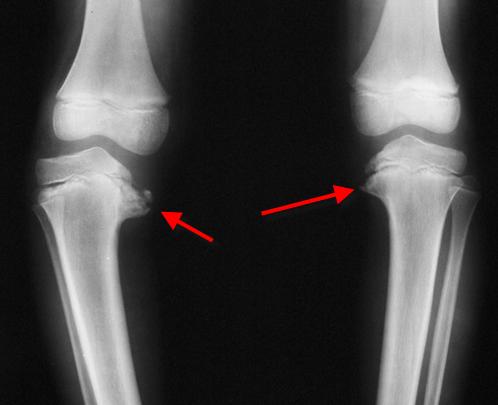
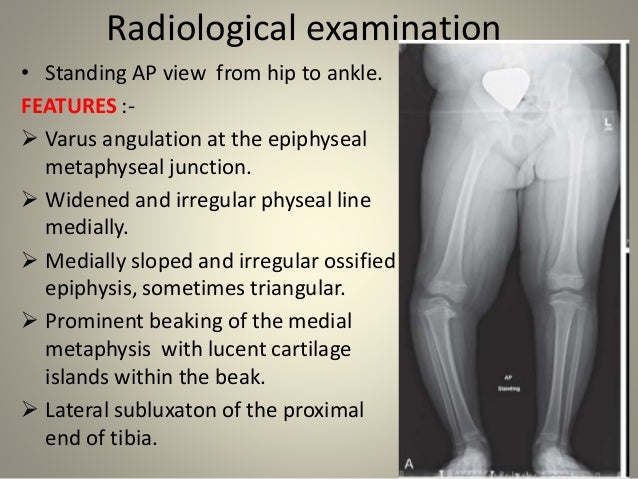
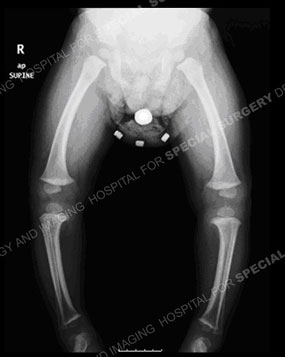
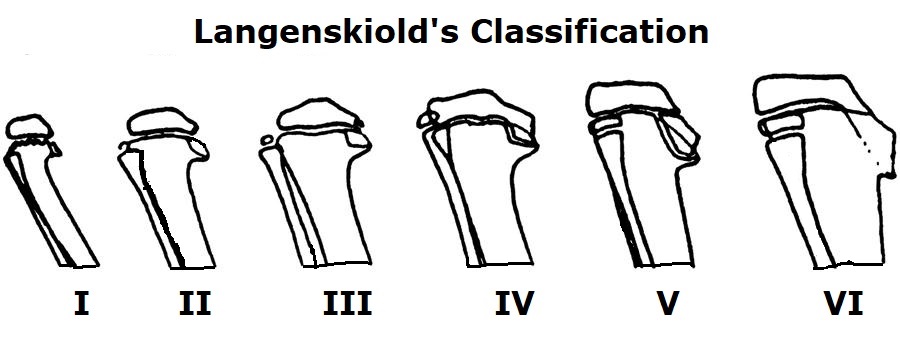
Infantile Blounts disease is progressive pathologic genu varum centered at the tibia in children 2 to 5 years of age. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with presence of a genu varumflexioninternal rotation deformity and confirmed radiographically with an increased metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle. Infantile early onset which is typically noted between 2 and 5 years of age and adolescent late onset which occurs after 10 years of age.
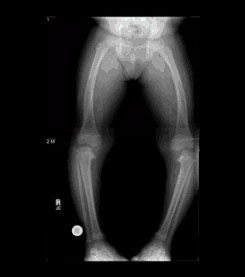
The disease causes the growth plate near the inside of the knee to either slow down or stop making new bone. Suggested causative factors Infection Trauma Osteonecrosis Latent form of rickets ALTHOUGH NONE HAVE BEEN PROVED Combination of developmental and hereditary factors is most likely the cause 7. Adolescents with Blounts disease are most likely to experience pain with the bowing.
1 Early OnsetInfantile Blounts Disease 1-3 years of age 2 Late Onset. Blounts disease is a condition found in children that affects the growth plates around the knee. The Relationship of early walking and obesity with Blount disease.
2 Forms of the disease. Juvenile Blounts Disease 4-10 years of age Adolescent Blounts Disease 10 years of age Cause is controversial and multifactorial hereditary or development factors Current theories. A small amount of bowing is actually quite normal in young infants.
Rickets deformities are related to either a deficiency of vitamin D in the diet or a genetic cause that leads to vitamin D metabolism disorders and is related to kidney disease. 1 2 There are two types of Blount disease early-onset and late-onset based on whether. It is also know as tibia vara.
Untreated infantile Blounts disease or untreated rickets results in progressive worsening of the bowing in later childhood and adolescence. Blount disease is a growth disorder of the shin bone tibia characterized by inward turning of the lower leg bowing that slowly worsens over time.
Infantile early onset which is typically noted between 2 and 5 years of age and adolescent late onset which occurs after 10 years of age.
Epidemiology There is no recognized inheritance pat. Blount disease is a growth disorder of the shin bone tibia characterized by inward turning of the lower leg bowing that slowly worsens over time. It can result from a vitamin D deficiency. 2 Forms of the disease. A small amount of bowing is actually quite normal in young infants. Rickets deformities lead to bow leggedness and must be distinguished from Blounts disease since the treatments are completely different. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with presence of a genu varumflexioninternal rotation deformity and confirmed radiographically with an increased metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle. Blounts disease is a condition found in children that affects the growth plates around the knee. However as most children begin to walk between the ages of 1 and 2 years old their legs gradually straighten out.
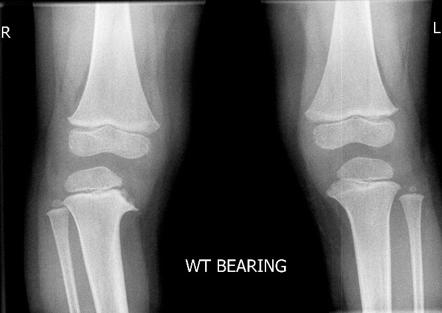
Likely differs for the different forms of the disease. Untreated infantile Blounts disease or untreated rickets results in progressive worsening of the bowing in later childhood and adolescence. Likely differs for the different forms of the disease. Blount disease also known as infantile tibia vara is characterized by bowing unilateral or bilateral and length discrepancy in the lower limbs see the image below. Epidemiology There is no recognized inheritance pat. It is also know as tibia vara. Moreover involvement of upper limbs and enlargement of costochondral junctions rickety rosary can differentiate rickets from Blounts disease.




























Post a Comment for "Blount Disease Vs Rickets"