The Most Common Clinical Syndrome Caused By A Block In B Cell Maturation Is
The most common clinical syndrome caused by a block in b cell maturation is. 35 Primary B-cell disorders may also result in lymphoproliferative diseases. This preview shows page 10 - 14 out of 14 pages. Most recently a mem-ber of the T-box transcription-factor family TBX1 has been implicated as a cause of most of the main signs of DiGeorge syndrome 1617.
The syndrome includes flushing and diarrhea and less frequently heart failure vomiting and bronchoconstriction. Minimal change disease is the most common cause of idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome. Lymphoma including Hodgkins disease.
The first and second most common B-cell disorders are IgA deficiency and CVID with incidence estimated at 1 case in. Which allows for the maturation of recipient T cells. Lymphoproliferative syndrome-2 also known as CD27 deficiency is an autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder associated with persistent symptomatic EBV viremia hypogammaglobulinemia and impairment in specific antibody function resulting from impaired T cell-dependent B-cell responses and T-cell dysfunction summary by van Montfrans et al.
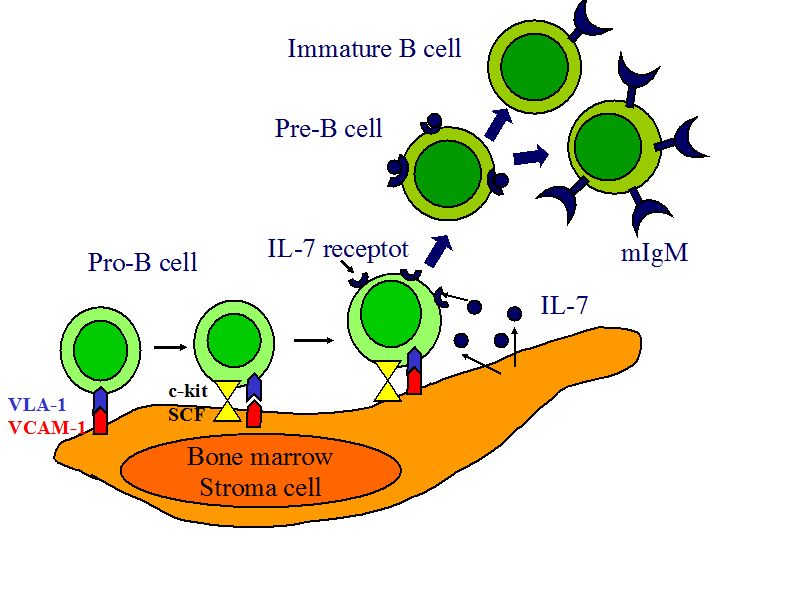
Injecting too low B. It is required for B cells to mature past Pre-B cell stage What is the most common clinical syndrome caused by a block in B cell maturation X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Vasculitis including systemic lupus erythematosus.
Pts The most common clinical syndrome caused by a block in B cell maturation is from HSC 4504 at University of South Florida. Carcinoid syndrome is a paraneoplastic syndrome comprising the signs and symptoms that occur secondary to carcinoid tumors. Segmental means damage affects only part of an individual glomerulus.
Many overwhelming infections both viral and bacterial may cause severe. The most common cause is idiopathic fibrosis and sclerosis of the conduction system. B cells are clonally expanded within the CNS producing intrathecal immunoglobulin IgG in various CNS disorders such as multiple sclerosis MS paraneoplastic CNS disorders and stiff-person.
Injecting too high 7. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is scarring in scattered regions of the kidney.
Pts The most common clinical syndrome caused by a block in B cell maturation is from HSC 4504 at University of South Florida.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis can develop where there is ascites present. The most notable of the causative organisms are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. Which one of the following are not used in water fluoridation. This is a frequent development. Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the beta globin gene that leads to faulty hemoglobin protein called hemoglobin S. The most common infection is peritonitis followed by lung skin and urinary infections meningoencephalitis and in the most serious cases septicaemia. This preview shows page 10 - 14 out of 14 pages. Lymphoproliferative syndrome-2 also known as CD27 deficiency is an autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder associated with persistent symptomatic EBV viremia hypogammaglobulinemia and impairment in specific antibody function resulting from impaired T cell-dependent B-cell responses and T-cell dysfunction summary by van Montfrans et al. Several candidates for the genetic defect in DiGeorge syndrome have been identified.
Which one of the following are not used in water fluoridation. Focal means that only some of the glomeruli become scarred. Injecting too low B. Genetic defects also affect the signal-transduction. Which allows for the maturation of recipient T cells. Hemoglobin S changes flexible red blood cells into rigid sickle-shaped cells. Numerous systemic diseases are associated with neuropathy.




















Post a Comment for "The Most Common Clinical Syndrome Caused By A Block In B Cell Maturation Is"